RFID Solutions vs. Business Solutions with RFID: Toward Operational Excellence
We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, then, is not an act, but a habit
Aristotle
Executive management of numerous companies have successfully implemented Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) solutions to improve inventory management, increase visibility in supply chain, create customer value and advance competitiveness in the global marketplace.
The majority of these solutions are using a unique ID code and digital memory storing small amounts of data. However, these two built-in RFID features are only a fraction of the full capabilities of RFID. This underutilization is limiting RFID potentially high positive impact on business performance and the drive toward Operational Excellence (OPEX).
Fortunately, companies practically in any industry can get significant benefits in terms of “Profit to Loss” ratio by developing and implementing business solutions based on synergy between two or more technologies combined with RFID.
This article will explore the challenges and benefits of a variety of RFID applications and the resulting profit maximization.
RFID Market Drivers
For decades, new technologies have been the essential tools for business performance improvement. One of the technologies, – RFID has become a recognized as an important enabler of business growth, with more companies adopting RFID solutions.
However, only a small portion of RFID applications completely realizes its technological capabilities. This fact perhaps leads to an underestimation of the market segmented compound annual growth rate (CAGR). If the RFID character changes from “supporting applications” to “building blocks” for solutions aimed at maximizing business improvement, the RFID market will probably grow even faster.
A partial list of RFID market drivers selected by “Supporting Application” criterion includes:
- Customer Service
- “… When it comes to keeping your existing customers, customer service is three times more important than price—and five times more important than functionality.”
Source: How the World Sees You: Discover Your Highest Value through the Science of Fascination”, Sally Hogshead; Harper Business, 2014 - SIXT [German car rental agencies] Finds RFID Is Key to Improving Customer Service”, RFID system shrinks car key search, requires only 20 seconds.
Source: RFID Journal LLC., Nov 10, 2014
- Industrial Sector: Rising Demand for Instant Asset Tracking of equipment, tools and inventory
RFID Market for Industrial Applications: 2016-2020, TECHNAVIO, CAGR of 19.2%,
Global RFID Market for Industrial Applications 2016-2020, Research and Markets of Dublin, 2016
- Transportation Sector: Ticketing, RFID Electronic Ticket System
- Retail Sector: Apparel item marking
- According to Francisco Melo, VP, global RFID, Avery Dennison 2016, over 50% of leading apparel retailers globally are assessing, testing or adopting RFID
- Analysis of the Global RFID Market in Retail, Frost & Sullivan, 09-Mar-2015
CAGR of 38.9% between 2013 and 2020
- Supply Chain Management Sector:
Incorrect data flow and inventory unaccountability in retail applications
- Healthcare Sector: Missing medical equipment and instruments; focus on infection control
- Technology Convergence to Pave Way for New Applications
Source: Frost & Sullivan, Report, 31-Mar-2016
- Blood Monitoring Systems Market Drivers, Trends & Challenges 2016-2020 Research and Markets, Sep 28, 2016; CAGR of 22.96% between 2016 and 2020
- Global RFID Smart Cabinet Market 2016-2020
TECHNAVIO, Market CAGR of 14.03% from 2016 to 2020
- Pharmaceutical Sector: Anti-Counterfeit Market
- RFID Tags Market Trends, Global Industry Analysts, Inc., projected RFID tags sale to reach US$6.9 billion by 2020
- Anti-counterfeit packaging market, WHATECH, Market size will grow from $82.05 B in 2015 to reach $153.95 B by 2020; CAGR of 13.41% to 2020
- Food Production Sector: Improving Safety, Compliance and Processes;
- Global RFID Smart Cabinet Market 2016-2020
Technavio; CAGR of 14.03% during the period 2016-2020
- Optimizing Efficiency in the Supply Chain and Retail Stores
Global Packaged Food Traceability Market 2016-2020
Research and Markets, CAGR of 8% by 2020
- RFID in the Global Smart Cold Chain Market, Frost & Sullivan, 22-Jul-2016
The common drivers influencing all sectors include:
- Security & Access Control Sector – dominates the RFID Tags Market
RFID Tags Market Trends, Global Industry Analysts, Inc., 2016
- Logical reasons and emotional motivations to acquire new RFID innovative technologies – expecting profit increase and gain prestige, brand strength, and a leader reputation
- Internet of Things (IoT): RFID functions are a fundament for IoT
- Market Outlook and Forecasts 2016 – 2021, Mind Commerce: June 2016
- RFID in the Global Manufacturing Market, Frost & Sullivan Report: 20-Apr-2016
- Standards, Regulations & Mandates —Government mandates for the tracking of livestock; Government of various countries such as US, UK, China etc. have mandated use of RFID for projects related to citizen identification and counterfeiting.
RFID Market: Global Industry Analysis and Opportunity Assessment 2015 – 2025
Future Market Insights, December 2016
Open standards are becoming available—notably the new ISO 18000 EPC Types 3 and 4, and IEEE 802.15.4
- Data entry: Error reduction with RFID solutions
- Inventory Visibility & Management RFID increases inventory visibility from 50%-60% to above 90%.
- “Radio Frequency Identification Market (RFID) to CAGR of 11% 2016-2020”
RNR Market Research, 06/08/2016
- “TECHNAVIO Identifies the Top Four Drivers for the Global RFID Systems Market Until 2020” TECHNAVIO, 02 Sep 2016
- Rapid adoption of RFID in various sectors and lowering cost of RFID components
RFID Market 2016 in APAC Trends, Market Share, Industry Size, Growth, Opportunities, and Market Forecast to 2020
RFID Market Challenges may include:
- Low awareness among potential users about available solutions
- High initial investment and pricing
- High equipment maintenance costs
- Globalization of consumer markets
- Reduced customer loyalty (‘smart shoppers’)
- Increase of an enforced competition strategies for process-based businesses
Business Challenges & Issues
All business improvement initiatives face specific and common challenges and issues in different industries. Common subjects may be:
- Slow move toward Operational Excellence
- Financial losses from theft of materials, tools, and equipment
- Potential threats to public health from Hazardous Materials
- Low Logistics & Supply Chain visibility and performance
- Long Time spend for Managing Stock Rooms
- Low Fixed Asset effectiveness and equipment short interval of MTBF
- Deficient Operating & Production efficiency
- Personnel injuries, wrong procedures, and damage of equipment
- Regulatory incompliance
Subjects listed below relate to a specific industry sectors:
Construction
- Long Construction Cycle Time that is money to owners, builders, and users
- Slower adoption of technical innovations
- Unpredictable construction processes
- Complicated management and supply utilities
- Significant Labor consuming for periodic items inspection (safety operation in accordance with ANSI and OSHA requirements)
- High Labor Processing Cost
- Elevated volume of Paperwork, Costly paper-based processes
RFID-based solutions enable some improvement of construction processes and eliminate customers’ frustrations by better tracking materials and all data, as well as present it to regulatory agencies.
Manufacturing
- Difficulties in dynamic resources allocation for numerous activities
- High labor cost and long operational time
- Inefficient material handling and production control
- Inadequate practice of equipment maintenance management
- Multiple Errors in manual data collection and document control
- Late reaction of Quality Control
- Infrequent performance analysis
Pharmaceutical
- Counterfeiting
- Susceptibility of brand integrity
- Expensive extreme measures for product safety
- Missing expiration dates
The FDA has recommended RFID to combat counterfeiting of pharmaceutical products by implementing ‘product pedigree’. The directive includes compliance with specified transportation conditions:
- maintaining integrity of the cold chain
- detecting harmful environmental factors
- providing evidence of tampering (contamination) for the purpose of extortion
Healthcare
- Long time for Emergency Response
- Large number of adverse events related to medication, procedures, infections
- High cost of patients care (laboratory and supplies)
- Overload personal and nurses
Retail
- Lost sales due to out of stock items
- Inventory inaccuracies
- Fraudulent returns of merchandises
- Losses due to unknown customers’ shopping behavior and floor paths
Warehousing
- Unproductive truck load planning, routing, scheduling and wrong deliveries
- Long handling time of arriving shipments
- Inefficient inventory control
Food production
- Unreliable integrity preservation of the cold supply chain
- Inability to detect and warn of record tampering of expiration dates
- Work force incompliance to regulations
Implementation of RFID solutions in food production and distribution can ensure safe packaging and products delivery. It may effectively overcome most of the listed above challenges and issues and assure operations scheduling and production control, process safety and interlocking.
RFID Solutions for Business
Electronic devices based on principles of RF Identification surround us everywhere. Mobile phones, TV RF remote controls, Wi-Fi, automotive immobilizers, keyless entry and engine remote starters, garage door openers, automated toll payment systems, aircraft identification.
Each of these applications uses unique and unchangeable codes for identification in a wireless data exchange and contained in a Transponder. The name comes from a combination of two words: Transmit and Respond. Transponders in a simple form are electronic devices having an IC memory keeping a unique, unchangeable identification number and storing and retrieving customer data. In addition to Transponders (aka Tags), conventional RFID systems usually include three more major components:
- Readers are an integrated transmitters and receivers (transceivers) that provide data communications
- Antennas are a reciprocal devices that converts electro-magnetic waves in electric current and electric current into electro-magnetic waves
- RFID Printer–Encoders are specialized printers capable of encoding transponders with EPC and customer data and printing visible information on Smart Labels and RFID Smart cards.
RFID systems can work at different frequency bands. Among allocated by FCC frequency bands for RFID, four are most popular: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), Very High Frequency (VHF) and Ultra High Frequency (UHF). Each RFID frequency band has specific features of radio waves in respect to propagation, penetration abilities, physical application conditions and different resilience to negative environmental impacts. A great variety of available transponders allow for a large diversity of RFID applications.
For example, by supplying materials, sub-assemblies or material containers with unique RFID tags, manufacturing can automatically confirm that all preceding procedures were completed correctly before the next manufacturing phase. Furthermore, date of production order and condition parameters may be stored in RFID tags’ memory at the beginning and then manually or automatically verified and updated at several places, providing fast local data maintenance and an entire process redundancy. The RFID-based tracking of parts, devices and pallets can lead to improved shipment and inventory management. Complete data about the production process helps reduce labor costs and accelerating the overall manufacturing process.
Benefits of RFID Integration
RFID can create considerable values at least in three areas of enterprises: Business, Technology and Processing
Business benefits:
- Reduce investment in machinery, tools & equipment
- Decrease expenses on Assets Management & Maintenance
- Minimize costs of Waste Management
- Extend & simplify Customer Service
- Maximize operational Profit/Loss ratio
- Condense time and labor workload in warehousing and supply chain
- Validate products advancement over rivals
- Deliver Brand Strength & Competitive Advantage
Technological benefits:
- Assure stock accuracy and block Theft & Shrinkage
- Enable M2M communications and Industrial IoT
- Improve Environment Protection
- Support Regulatory Compliance actions
- Manage consistency in data collection, calculations, and distribution
- Provide extremely secured Access Control
Processing enhancement benefits:
- Ensure highest Work Safety
- Exclude errors on assembly lines and rework volume
- Automate Warehouse Operation, Material Handling & Inventory
- Avoid negligent service in hospitals and Assisted Living centers
- Enable faultless medication distribution in Healthcare
- Boost efficiency and effectiveness of people work & Equipment
The following examples illustrate benefits of RFID practical applications:
Access Control/Security
Time and attendance
- By supplying authorized employees with RFID transponders in form of credit card or key fob, companies save significant time for granting or rejecting access at doors, entries, or turnstiles. In addition, data from ID cards permits time recording of accessed days.
- In facilities with high security requirements such as military, medical and pharmaceutical, RFID practice includes fast authorization and verification of personnel. Operation phases for entering data into the IT system or documenting the production progression becomes noticeably shorter than manual recording.
- At large conferences, an RFID “Attendee Solution” eliminates waiting time for visitor registration lines at entrances and increase customers satisfaction.
Parking
The Canadian company GAO RFID has launched an Enhanced Hands-Free Advanced Parking Solution that simplifies service of parking lot and reduces service cost.
Anti Counterfeiting
Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceutical companies have embedded RFID chips in drug containers to track and avert the theft of highly controlled drugs, such as OxyContin.
Finance
The European Central Bank is considering embedding RFID chips in Euro notes to combat counterfeiters and money-launderers. This also would enable banks to count large amounts of cash in seconds.
Asset Tracking & Tracing
Do not be confused by an “Asset Track and Trace” term, sometimes incorrectly referred to as “Asset Management” – the optimization of fixed asset usage.
Airlines
United Airlines uses RFID tags to track passenger bags, while Delta Airlines is tagging customer bags with RFID to reduce the number of lost bags and make it easier to route bags if customers change their flight plans. A report from IATA and SITA predicts that global RFID use by Delta Air Lines and other carriers to manage bags will save $3 billion by the end of 2022, and reduce handling errors by 25 percent.
Warehousing
According to “RFID Journal LLC”, East Coast Warehouse – the temperature-controlled warehouse operator has seen a 19 percent increase in productivity since installing RFID system that uses passive UHF tags to track containers movement. The operator has reduced labor costs and boosted productivity via RFID solution that tracks the locations of more than 1,000 shipping containers throughout its 60-acre yard.
Logistics & Supply Chain
- Logistics Company DHL, part of Deutsche Post DHL, reported that its GPS-and RFID-enabled DHL Smart Sensor solution has tracked more than one million health-care and drug shipments since 2010. Customers can monitor highly sensitive life sciences and health-care freight throughout the supply chain. It helps ensure cargo safety and integrity for critical temperature-controlled products.
- Three seaport operators in the United States, which account for 70 percent of the world’s port operations, agreed to deploy RFID tags to track daily arriving containers.
- The U.S. Department of Defense is planning to use RFID technology to trace military supply shipments.
- SWISS rail freight operator “SBB Cargo” is equipping its entire fleet of freight wagons with RFID devices in respond to customers demand. Customers will be able to follow the progress of their wagons on the railway network and the time of arrival or departure.
Healthcare
- In automated RFID anesthesia care, each medication package has an RFID tag that keeps in its memory a unique serial number and data specific to that drug. Anesthesiologists acknowledge that this automation considerably lowers their time recording this data during surgical procedures. In addition, using “Medication RFID Cabinet” solution provides real time inventory of items in stock, including recording when an item was entered into stock, its lot number and expiration date and when an item was removed from stock to be used.
- “En-Vision America Company” has developed for visually impaired people the ScriptTalk Station RFID solution that retrieves information contained a Talking Labels affixed to prescription containers and uses a synthesized voice to “read” prescription information and instructions for their prescription medications.
- University of Vermont Medical Center, an academic medical headquarters in Burlington, has tracked more than 5 million medications using RFID labels in 2015. These Smart Labels help save time and reduce errors.
Utility
“Bravo Environmental”, a Seattle-based underground utility maintenance company is burying an RFID tag at each location it accesses underground. The company implemented RFID to automate recording time of advert events and help personnel and customers to locate a particular pipe, conduit or underground cable saving tremendous time and labor.
Transportation
Many tolls roads in the United States use RFID technology to collect fees without the need for tollbooth personnel and provide “Non-Stop” convenience for drivers.
INVENTORY CONTROL
Library Systems
- An RFID library solution improves the efficiency of circulation operations. Check-in, checkout and automated inventory of books on the shelf reduce the library’s staff time spent on these activities by up to 45%.
- RFID inventory application is now tracking, managing and securing the Vatican Library’s priceless collection of 2 million books and manuscripts.
- Estonian National Museum (Tartu) has installed more than 600 RFID-enabled signs produced by Taiwan-based “E Ink”. Each visitor gets an RFID card that at close proximity activates the display of exhibit-related information in selected language.
Rental Management
- Large companies like, for example, casinos often manage thousands of employee uniforms. They need to track each uniform assigned to a specific employee, the age of uniform, the number of times washed. An RFID laundry management system performs these tasks and identifies missing uniforms.
- On-line formal wear rental leader “The Black Tux” integrated an RFID solution from Fujitsu to reduce rental costs, speed delivery, and enhance customer experience by improving order accuracy and reducing internal handling and administrative expenses. The solution uses RFID tags made of transparent materials sewn into garments and accessories.
Construction
Construction workers use a large variety of fasteners, tools, and other instruments. Having these assets available when needed significantly increases
- efficiency of production and saves time. RFID Tool Tracking Systems enables identification of whom and when a tool was taken and indicates when the tool was returned.Automotive
- Michelin, Goodyear and other tire companies are seeking ISO ratification of four global RFID standards that will specify a position of RFID tags and their encoding and testing procedures.
- Goodyear introduced the company’s first commercial use of RFID in truck tires. Fleet operators can use this solution to reduce downtime by ensuring accuracy, improving tire management and security. This application is also beneficial to Stock Control of new, used and retreaded tires accelerating identifications and records without mistakes.
Aerospace
- Technical personnel use RFID tags for storing maintenance records in tags’ memories. After servicing the units, technicians update tags with the latest information in effect creating a decentralized DB. This RFID solution creates an accurate audit trail throughout the units’ lifecycle.
Retail
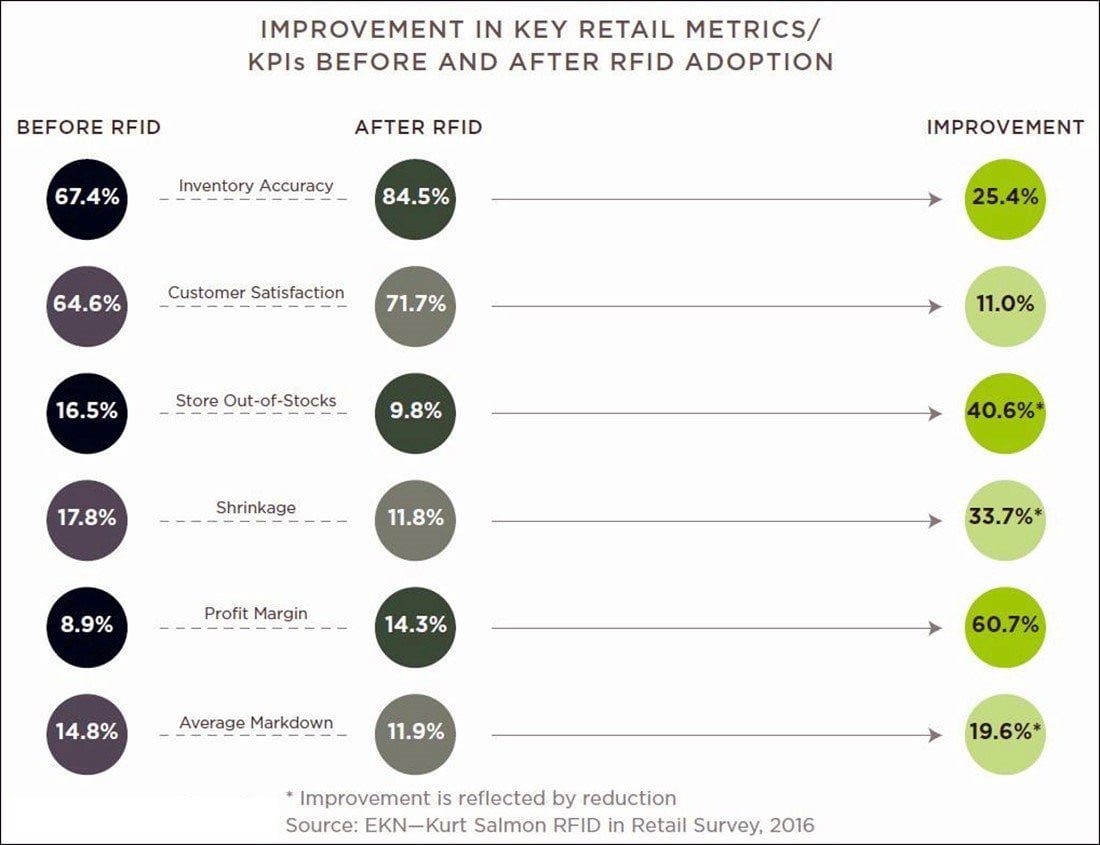
According to retail survey, conducted by EKN-Kurt Salmon, RFID implementation has been very beneficial (a chart on the left depicts results).
- Before Marc O’ Polo introduced RFID solution to its stores, taking inventory had typically required 20 employees for a full eight-hour shift. Now, only four employees can complete the process in about one hour.
- Macy’s, have experimented with item-level RFID for apparel and footwear. Early pilots have achieved some excellent results. This application is also good for back rooms of large-box retailers.
Manufacturing
- Car-cover Manufacturers are Tracking Work-in-Progress via RFID. The companies use a “Near Field Communication” (NFC) -based system from SHOP FLOOR to view a completion of each task by different stations, in order to identify assembly bottlenecks, facilitate quality control and monitor worker productivity.
- LCD flat screen manufacturing company “INNOLUX” installed a passive UHF RFID system to track the arrivals and departures of vehicles and palletized goods at one of its plants in Taiwan. Since the installation, company has boosted efficiency and reduced frequency of errors related to the wrong dock door pick-up and difficulties of locating merchandises.
Shown above examples of RFID solutions based on transponders ID uniqueness have definitely proved to be useful for businesses improvement. However, they are missing a dynamic that is absolutely needed for some critical business areas, especially in operational control where timing is vital.
Perhaps, you want to advance your business by implementing new technologies and you know exactly what you need. To realize your project, you might hire a systems integrator or contractor to implement your plan. Conversely, if you want to realize improvements by utilizing, for example, an RFID technology, which is outside your area of expertise, then most likely you will seek a professional assistance. You can select professionals from system integrators, consultants, or both kinds. Without them, RFID implementation could become a long-lasting expensive experiment with a less than desired outcome. It happens often because real solutions based on RFID technology are usually very specific to application conditions. They might include environment, material and dimensions of surrounding objects and operating facility structure.
Finding the right adviser to develop an effective business solution based on RFID – is critical to producing a working system implemented on time, on budget and providing a positive return on investment. The adviser can determine the hardware and software products best suited for each unique situation. More often than not, vendors propose prepared RFID solutions just because of their earlier successful implementations. Sometimes system integrators are seeking in client businesses the troubling spots, which fit their solutions instead of developing solutions for a significant business improvement.
Here are a few things to look for.
- RF Engineering: Are consultants fluent in wireless data communication fundamentals? Have they done a significant amount of wireless sub-system development? Will they be open to suggestions and changes requests?
- Experience with antennas and propagation
Now that you have found a consulting firm or consultant, are they professionals in designing antennas for long and close proximity RFID applications?
- Experience in business
Do they have enough passion to understand RFID peculiarities that will make your business solution outstanding? Can they design and develop a customized solution using RFID and other technologies aimed at maximizing your P/L ratio?
- Creativity and inventiveness:
Can they come up with innovative and effective design? Are they capable of developing IP and share it to preserve your competitive advantage?
- Technical competency: Are they knowledgeable of varieties of RFID technologies and Sensors available on the market? Can they bridge the gap between engineering are business language?
- Organized and motivated: Do they have capability to conceptualize business requirements and convert opinions into plainly ordered groups? Do they care about their brand and reputation and are they driven by a motivation to complete project on time and within budget?
- Service features:
Look for a firm or advisor-consultant who knows well vendors of HW & SW for RFID and can select and direct/supervise a solution implementation. This speeds the entire process. In addition, it is beneficial to work with a firm, which has been deeply involved in RFID Technology developments first-hand. This will save time and expenses on strait solution building instead of “remunerating some consultants while they learn”.
Business Improvement Solutions with RFID
According to surveys conducted by leading professional analytical firms in 2016 (KPMG, Gartner, Conference Board Inc., PWC) an Operational Excellence, year after year, remains one of the five top priorities of CxO suite for business improvement and for the good reasons.
For example, a study by the Board of Manufacturing and Engineering Design of the U.S. National Research Council has shown that companies that effectively implemented most advanced manufacturing systems (based on principles of Operational Excellence) achieved tremendous improvements in asset productivity performance:
- Increase in product quality 100–400%
- Increase in manufacturing productivity 40–70% (quantity/person)
- Increase in manufacturing capacity 15–25%
- Reduction in in-process inventory 30–60%
- Reduction in overall product introduction time 30–60%
OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE – WHAT IS IT?
The common definition of Operational Excellence (OPEX) is:
OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE IMPLIES THAT AN ENTERPRISE IS RUNNING OPERATIONS IN THE BEST POSSIBLE WAY
“The best possible way” changes over time in response to current business conditions and technological advancements. In contrast with a “business efficiency concept”, which specifies to run operations activities safely and well, OPEX describes improving performance by safely executing the right activities exceptionally well at the right time. Therefore, the timing here is a critical factor for a successful operation.
Before we move further and discuss why RFID is an important building block for solutions targeting a business drive toward OPEX, let us discuss one of concepts of Operational Excellence.
OPEX ASYMPTOTE CONCEPT
Among many OPEX discussions, one is concerned whether OPEX is achievable or not.
By assuming the OPEX attainability concept, we are admitting that there is no room or need for further business improvements. However, once achieved, excellence does not last forever. If you maintain a status-quo of this once achieved performance, your business will not sustain P/L ratio growth. Remaining competitive in a changing, global marketplace requires periodic operational performance reviews and adjustments to keep business viable and competitive.
One of Albert Einstein’s quotes was “Doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result is Insanity”.
What is competitive and optimal today will not be the same tomorrow. Besides implementing available internal improvements, investing in innovative technologies will ensure an accelerated performance growth toward the next optimum.
OPEX embraces at least four most important groups for optimization in:
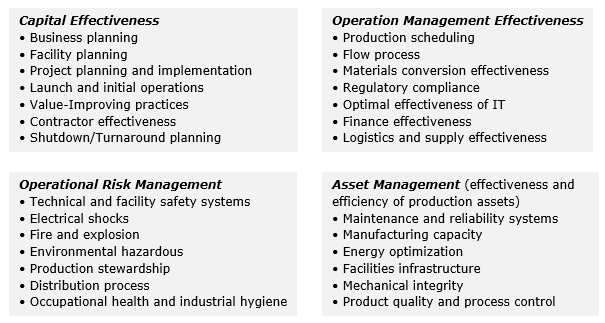
The chart below introduces an asymptotic concept for OPEX. It is not for the whole operation but rather for optimum performance levels for each group. It is worth to mention, that an OPEX level itself also moves up over time and outdates achieved optimums.
An asymptotic OPEX concept may lead to three strategic conclusions.
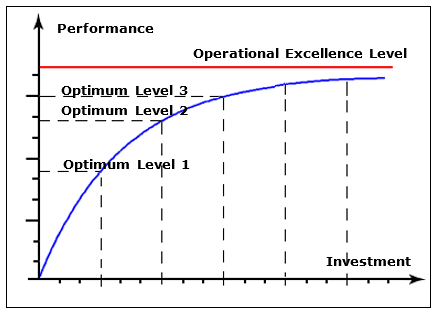
- The initial investment for operational improvement ensures a significant rise in business performance and a big step toward OPEX. That is what early adapters gain from new technologies implementations
- In order to take advantage of new technology, businesses must identify first the bottleneck in operations management where innovating solutions will have the greatest effect.
- Every next equal investment in performance enhancement adds less and less to improvement results. In other words, every next equal improvement will require a much higher investment than the previous one.
KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS (KPI)
To conclude whether a company’s operational performance has been successful (acceptable) or not, management uses a set of performance parameters or KPI and compares them with thresholds that set a benchmark. Historically, Accounting was a source for KPIs estimations.
According to the Journal of Management Accounting, Management Accounting Research in the US started in the 1950s in response to the Ford Foundation’s efforts to help their management with control functions by providing expertise in financial reporting. Since that time, Accounting has established very reliable metrics for business performance analysis. A set of measurements covers practically every business department.
For example, more than 25 KPIs from accounting practice represent the essential operational aspects of logistics to highlight operational issues. Raw Material Inventory Turns, Raw Material Content, Finished Goods Inventory Turns, Obsolete Inventory.
Percentage, Inventory Accuracy, Picking Accuracy for Assembled Products are just a few samples.
The other KPIs for analysis of Production department use measurements obtained from Tracking Systems for Units of Production, Machinery Utilization Time, and Scrap Tracking.
Another set of KPIs includes Constraint Rework Percentage, Constraint Schedule Attainment, Throughput Effectiveness, Manufacturing Efficiency and Effectiveness, Productivity Index, Average Equipment Setup Time, Unscheduled Machine Downtime Percentage and MTBF.
In contemporary business, despite of efficiency, Financial and Managerial Accountings can provide only monthly closing reports from the ERP system in a few days after the end of the month. During this month, management had no real-time visibility into where and when business has made and dropped earnings across its enterprises and in operations. Consequently, management can only make decisions affecting the future and is unable to take instant corrective actions against adverse events that have occurred.
Fortunately, business improvement solutions, utilizing a synergy of RFID with other technologies, are capable of obtaining all KPIs quickly. The fundamental approach of any control is Testing, Comparison and Feedback. Business solutions with RFID, for example in production, can help management make timely and correct control decisions. The information can include a status and trend line of processes at specific locations, not just be a large amount of unstructured Big Data. Instead, enterprise business solutions based on RFID are using Transponders as the decentralized Data Bases.
“VERSATILE RFID”
Versatile RFID is a methodology for business improvement that specifies a combination of RFID major components with other electronic devices, electro-mechanical structures, conveyors, and RF low power apparatus. Digital Data Loggers, specialized antennas, handheld and stationary Readers, GPS, Wi-Fi, Blue-Tooth interface and mobile phones with NFC are solutions building blocks. Integration of RFID transponders and simple microprocessors is almost ideal for processing historical information obtained by different sensors. A Wi-Fi addition to RFID enables retrieval of all collected data and trend lines on demand.
Instead of filling a matching spot in your business by conventional RFID solutions, a Versatile RFID approach allows for increase of P/L ratio for business. The achievements come from process optimizations, automation of functions, rising asset efficiency and effectiveness, assuring ultimate safety and protection of health and the environment.
Examples of business improvement with RFID:
Retail
Zebra Technologies has introduced its “SmartSense” System, which combines CCTV, micro-location and UHF RFID Readers. The system will help retailers to improve on-shelf availability, enhance the shopping experience, reduce shrinkage and boost sales. The RF devices, which mounted 50 feet apart in the ceiling, form a grid that provides RF energy to identify inventory items with embedded RFID transponders. The system is enabling retailers to obtain in real time information about events occurred inside the store.
Manufacturing
- Maintenance
An application following Versatile RFID principles can form an Activity or Error Log for equipment and simplify diagnosis, usage statistics and operating time counter, recording error codes utilizing a dual-interface transponder. A service specialist saves time and effort by remotely retrieving data using hand-held Reader or mobile phone with NFC, even from not powered equipment and without a direct access to internal compartment. The same application enables setting or reprogramming machines and equipment in advance before they turn-on. Widespread use of mobile phones with integrated NFC allows for substitution of the hand-held RFID Readers and opens huge opportunities for new RFID applications development.
- Production floor
Often, employees manually move many sub-assemblies around the production floor from one to the next production station. RFID can make the production floor transparent, by attaching to pallets the transponders, which contain information about all processes that have completed before. It also confirms a proper delivery.
Healthcare
Smart cabinets
According to TECHNAVIO, a leading research and advisory company, Healthcare sector is the main end-user of RFID Smart Cabinets. On an average, a hospital loses more than 15% of its assets in a year due to fraud or misplacement of hospital supplies. By utilizing RFID smart cabinets, hospitals reduce manual efforts in maintaining, tracking, and managing inventory. RFID system detects any device arriving to or departing from the cabinet. Authorized personnel can get instant status of a cabinet’s content.
Compliance
Transportation and food safety
In Cold Chain Logistics, many carrier companies use refrigerated trucks to deliver pharmaceutical products and perishable foods. Chasing fuel efficiency of refrigerated transport, some truckers turned off cooling equipment and turned it back on just before delivery. The actual climate conditions caused financial losses.
To verify the transportation compliance, shipping companies started using RFID digital data-loggers with gas, pressure, temperature and humidity sensors mounted inside the boxes to accumulate real-time environmental data. After arrival, a supply chain inspector with RFID Reader can retrieve remotely historical data. Currently, advanced companies are combining RFID data-loggers with communication devices in order to transmit real-time data, thus enabling preventive actions to save products.
Visit our website www.rfxvalue.com for more information.
By Boris Y. Tsirline
Boris is an innovative and inventive RFID Technologies expert, who is assisting companies with business initiatives to improve performance and move toward Operational Excellence. Connect with him on LinkedIn.