The Future of Supply chain: A digitized Supply Chain
The economy is at the beginning of the next major industrial revolution, and technology is the driver, this time as the heart of both the production of many different products and as a core intelligent component of the things we use every day.
Digitization has long since moved into factories, and is now enabling operations in which humans work side by side with intelligent machines.
“Industry 4.0” is the catchphrase widely used to describe digital networking in the manufacturing industry. Industry 4.0 is the fourth industrial revolution after the mechanization of production in the 18th century, the electrification of production and the introduction of assembly lines in the late 19th century, and, finally, the automation of production beginning in the 1970 s and continuing ever since.
This fourth revolution is set to raise automation to a new level, marked by the unstoppable march of information technology through all areas of industry, also known as the Internet of Things.
Now businesses are gearing up to invest almost a trillion dollars a year in the digitization of production according to a global study by PricewaterhouseCoopers based on answers from managers of more than 2000 companies in nine areas of industry.
Over the last two to three years, many companies across all industries have made major strides in this transformation process. Innovative developments in fields of artificial intelligence, virtual reality or smart factories, to name only a few, are already showing great promise in execution.
It is clear that Industry 4.0 is and will remain a major business and societal topic for the foreseeable future in all industries.
In my experience from leading a consulting company for various industries in several countries, I have seen how digital technologies have become part and parcel of serving customers around the world, optimizing a vast global supply chain, logistics operations and information services operations.
Even though these technologies are often behind the scenes, they impact our lives every day and are blazing a trail for Industry 4.0.
We recognize the potential of digital technologies to advance every part of a company, especially in areas such as logistics, engineering, production, procurement, supply chain, marketing and sales.
That is why, I will give examples in this article of how digitization is already changing how we work almost every industry, as well as share insights about both the opportunities and challenges for the future.
In this context I need to mention that I came across many concepts that I would like to share with practitioners: IOT, Data Analytics, Digitization, IIOT, AI, Deep Learning, Machine Learning, Computer Vision, RPA, Digitized Supply Chain, Big Data, Augmented Reality, 3D Printing, Cloud Based Applications and of course the so-in now Block Chains.
This article only focuses on Digitized Supply Chain, while the rest of the terms will be handles separately in a series of complementing articles
What each supply chainer from C level to juniors in any organization needs to know is that change is inevitable and that we can’t afford to be left behind.
In the last 20 years several new best practices have been created and adopted by many companies in Supply Chain such as: agility, collaborative planning, innovative supply chain, visibility, RFID, data networking, individualized products and services. Such practices have been easier said than done for many companies across the globe; the implementation was not as indented in many of the cases.
Adapting to digital supply chain can enhance all those practices.
Through adapting digital technologies in products and service supply chains businesses become unique and profitable. Computer chips are nowadays embedded in all sorts of items from refrigerators to clothing.
Instead of living in isolated islands, companies digitize everything to have real time data, visibility and insights. A related example to share here is Amazon Go Supermarkets.
Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JPm9StY7xx0
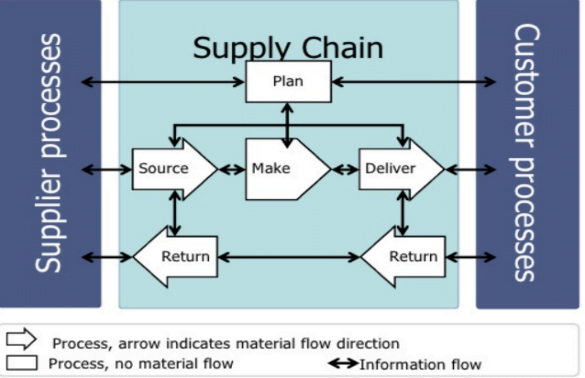
Traditional supply chains have horizontal information and physical flows. For example they follow the SCOR model (invented by Supply Chain Council, USA in the 1990s) of: Plan, Source, Make, Deliver, Return. (PSMDR). SCOR is a process framework maintained by the APICS Supply Chain Council. SCOR focuses on manufacturing supply chains but has been adapted for retail and service supply chains too.
SCOR organizes all the processes in a supply chain into six groups:
Plan: Decide what to make, when to make it, and where to make it.
Source: Buy the things that you need to make your products.
Make: Manufacture your products.
Deliver: Sell your products and get them to your customers.
Return: Take products back when they’re defective or need to be recycled.
Enable: Do everything else that is important for making a supply chain work but that doesn’t fit into one of the other groups. SCOR provides 5 performance attributes of supply chain and an extensive list of best practices. The customer orders are being taken care of through Deliver processes.
On the contrary in Digitized Supply Cain, the near future, customers are in the middle and central focus of all processes, where he traditional linear supply chain flow wouldn’t exist anymore.
Companies that are using computer systems to run their businesses with latest technology became more intelligent in real time decision making with higher profitability and bigger market share. And the opposite is true; companies who don’t adapt to technology are very slow in detecting changes and even slower in responding to changes.
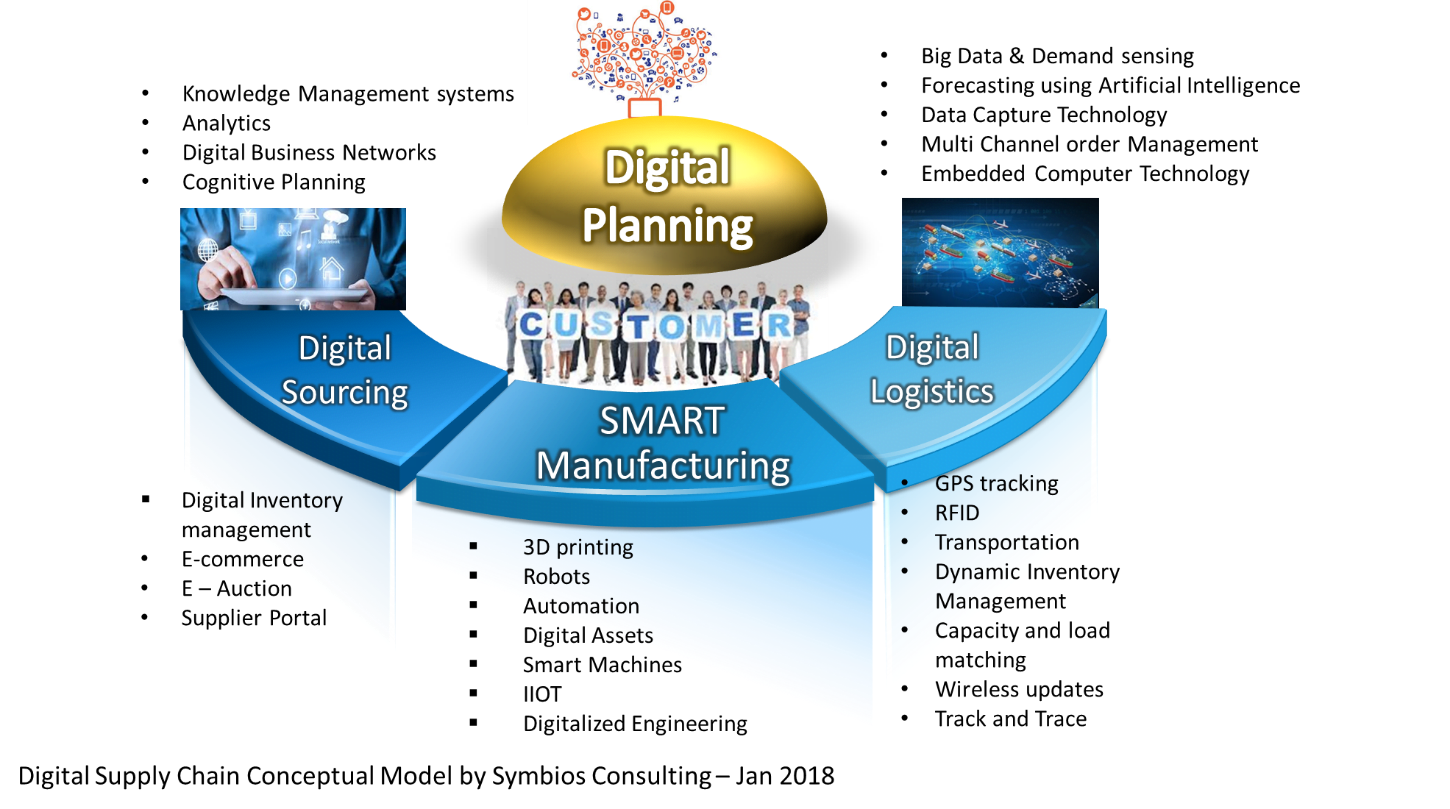
The below model shows a conceptual graphical illustration for Digital Supply Chain Management.
In digital supply chain the whole system is interconnected like an orchestra to convert from traditional linear model to a digitalized dynamic grid. Where customers are placed in heart of the supply chain, which typically consists of:
- Digital/ Intelligent planning
- Digital sourcing
- SMART manufacturing
- Digital Logistics/ e-logistics
A digital supply chain steeply leverages intelligence embedded in devices, analytics, external big data sources, and intelligent supply chain software to realize improved customer experience, increased value of products in the markets, generate new revenue streams and new markets and increase high profits.
A great example is Amazon Delivery Drones – unmanned airship to launch its delivery drones
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aYHKq3pwfE
In digital supply chain the whole system is interconnected like an orchestra to convert from traditional linear model to a digitalized dynamic grid. Where customers are in the place they like to be, at the heart of the supply chain.
The ultimate goal of digital supply chain is to become flexible and adaptable enough that a customized and personalized customer experience can be delivered.
While addressing cyber-security concerns and preparing for continuously increasing and inevitable risks, the Industry 4.0 transformation offers huge opportunities – for all industry segments.
Especially process industries who already have relatively high levels of automation. Digitization promises a major efficiency boost for production operations and maintenance as well as opens up new opportunities for the automated manufacture of flexible, highly differentiated product offerings. Moreover, research and development will benefit too. For example in areas including new material modeling simulation and analyzing research data as it has been done for many years in the high tech industry.
Secondly, industries are a part of a highly interconnected value chain. The interlinking and analysis of unimaginably large volumes of data, created not just within a company itself but within every step from raw material sourcing to end product usage in a customer’s product, raises transparency and drives monetary value to be realized.
The need for a holistic horizontal integration of all involved partners along the value chain is simply the next consequential step in the Industry 4.0 journey for supply networks to become ever more competitive.
The newly emergent data, processes and insights optimally coming from joint customer centric interfaces, which moreover should rely on joint decision making processes, will also give rise to new business models.
Thirdly, digitization forges deeper relationships between industry partners and their customers in many ways and offers huge opportunities for higher customer value and higher reliability towards ever changing customer needs. Digitization has already transformed many areas, and this is only the beginning.
The entire marketplace stands to benefit from perhaps the most important of all perspectives: digitalization will allow all to benefit from more effective and sustainable approaches to consuming planet earth’s precious resources! A world that is nearer than what anyone thinks, digitized and customer centric.
By Shereen Mossallam
Shereen Mosllam currently serves as the General Manager of Symbios Consulting. She is a qualified SCOR instructor & 20 keys consultant with a Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt, and has past experience in systems and quality engineering. Symbios Consulting Group delivers training in English & Arabic, and also delivers Lean, Six Sigma and Supply Chain consulting and deployment for each kind of business (manufacturing, , banking, healthcare, call centers,…..etc), in different countries: United Kingdom, Romania, Egypt, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Morroco, United Arab Emirates and Algeria.
Symbios Consulting is the preferred choice of companies who demand tangible results from value generation and waste elimination. Training and consultancy services were delivered to more than 200 companies worldwide with more than 1,000 Lean, Six sigma and Supply Chain projects for Green Belts, and Black Belts. Connect with Shereen on LinkedIn.